- Updated On: July 03, 2025
Community Solar Farm: Affordable Option for Renters and Low-Income Families
If you think that utilizing solar power is limited only to homeowners with spacious rooftops and cash in hand, you are wrong. A community solar farm is a practical and cost-effective alternative. It makes solar energy accessible to everyone, including renters and low-income homeowners. These off-site solar panel farms allow individuals to “subscribe” to a share of the farm’s energy production and receive credits. These credits lower their monthly electricity bill. No roof? No problem. Also, it allows those who do not qualify for a solar installation opportunity. These programs aim to provide opportunities for more people to benefit from clean energy. With rising utility rates and inflation, solar farms are becoming popular.

Let’s explore how solar farms work and what are the perks of subscribing to a community farm project. Also, we will highlight the states offering these programs.
What is a community solar farm?
Community solar farms give people access to solar energy without requiring them to pay any upfront cost or install equipment on their land. To power the surrounding homes and businesses, the electricity by a solar farm is delivered to the electric grid. Even if you live in a building with insufficient sunlight or rent a property that does not allow you to install a solar array on your rooftop, these farms make it easy for everyone to lower their energy cost by participating in a community solar project.
Despite 30% federal tax credit and solar incentives, there are many homeowners and small businesses who cannot either afford to go solar or there are other mitigating factors, such as renting, living in multi-tenant buildings, having roofs that aren’t suitable for a solar system, or other circumstances like HOA restrictions. Solar farms offer all of them an opportunity to access clean power and reduce their energy costs by subscribing to a community garden project. Moreover, almost anyone can participate in these projects who wants to avoid upfront expenses and onsite installation. Participating in a community solar farm is getting easier as this market develops.
How does a community farm works?
Community solar gardens are directly connected to your local electric grid, as opposed to standard rooftop solar. The nearby homes and businesses are powered by the electricity produced by the solar panels. The amount of clean energy provided to the electrical grid is measured using a meter. Your local utility company monitors that meter and makes sure that participants, also known as “subscribers,” gets credit for their energy bills.
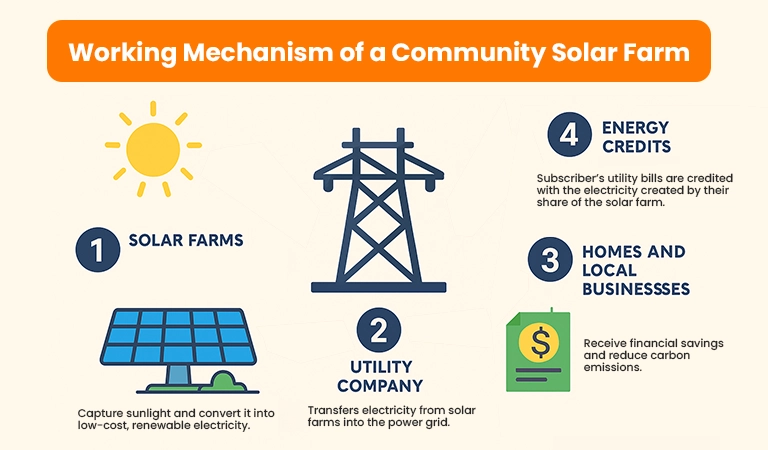
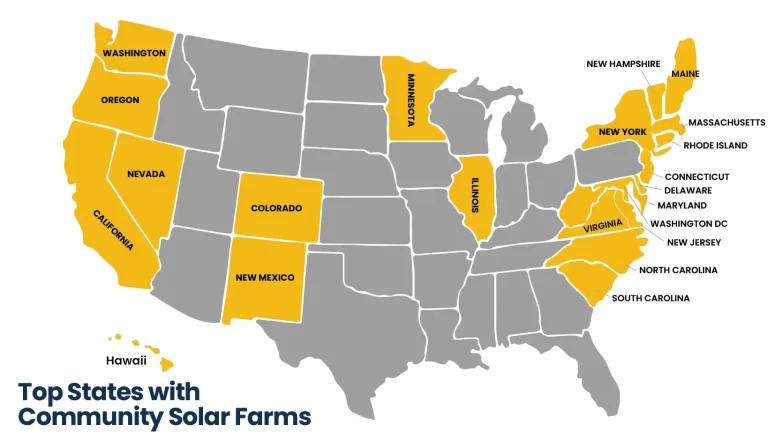
Which states are offering solar farms subscription programs?
There are community solar farms in 22 states and the District of Columbia that have passed shared renewables legislation. Also, it is possible to find community farms in areas where shared renewables initiatives are booming by small utilities and cooperatives.
What are the benefits of participating in a community solar project?
Solar gardens make clean energy affordable for all those who cannot invest in a residential solar system. The perks of participation are:

- Community solar is a goodway to go solar without the high cost of rooftop installation. No purchasing of panels, equipment mounted, or maintenance concerns, just subscribe and save.
- Subscribers usually get solar credits on their bill, lowering what they have to pay every month. However, savings differ depending on the area provider. However, most customers get huge savings on their electric bill, without having to change the way they use it.
- Unlike solar on roofs, community solar is ideal for renters, low-income individuals, and homeowners with shady or unsuitable roofs. It brings clean energy to those who would not be in a position to access it.
- Most community solar programs offer flexible contracts with no cancellation fee or long-term commitment. So, it’s a low-risk way to go solar with predictable savings and stable power.
- By subscribing, you’re promoting renewable energy production in your community. This reduces the consumption of fossil fuels and carbon emissions.
How do I participate in a community solar farm?
Membership in a community solar farm is as easy as enrolling in a local project, like leasing an apartment or subscribing to a streaming program. Depending on their annual energy requirements, a house or business enrolls in a project. There’s no down payment for enrollment. Instead, you commit to pay for the electricity your share of the solar array produces, usually lower than the credit you receive on your utility bill each month.
How much does the solar farm cost?
Like rooftop or commercial solar installation, the cost of developing a community solar farm depends on the location, system size, and solar panels and equipment brand. However, the solar incentives and tax credits offset the initial cost. In addition, there are several financing options available for these farms, such as power purchase agreements (PPAs) and community solar bonds, which can make the initial investment manageable. For example, a study by the Clean Energy States Alliance (CESA) shows that the Massachusetts-based solar community farm project financing was done through a combination of private investment, state and federal grants, and a loan from the Massachusetts Clean Energy Center. The project generated revenue through the sale of energy credits and PPA to a local utility.
Why choose a community solar program?
In a published report, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory states that 48% of businesses and homeowners are unable to use solar energy because they lack sufficient roof space or rent. Many other factors, including inadequate space, excessive shade, and zoning, make solar power unaffordable. In addition to financial advantages, community solar solutions are the solution to these problems and enable people to power communities with renewable energy.
In conclusion, there are many benefits of investing in a solar energy system. You will not only save on your electric bills but also reap the perks of solar incentives and local rebates. However, if you are not in a condition to buy a system, subscribing to a community solar farm is a good opportunity to lower your energy costs. These programs aim to make solar power accessible for everyone.
Related Articles:
As businesses seek reliable, cost-effective energy solutions, commercial solar emerges as a powerful alternative. Beyond reducing monthly utility bills, solar offers energy independence, protection from rising rates etc. Learn about top reasons and benefits!
You can participate in a community solar project regardless of whether you rent or do not have a suitable roof or if you prefer not to have equipment installed on your property. Explore everything you should know if you are planning to subscribe to a solar farm.
Solar farms are the workhorses of solar energy, taking up acres of land—sometimes thousands of acres—to produce clean energy for homes and businesses across the world!



