- Updated On: April 5, 2024
Solar Panel Farming: Boost Crop Yield Using Sustainable Energy
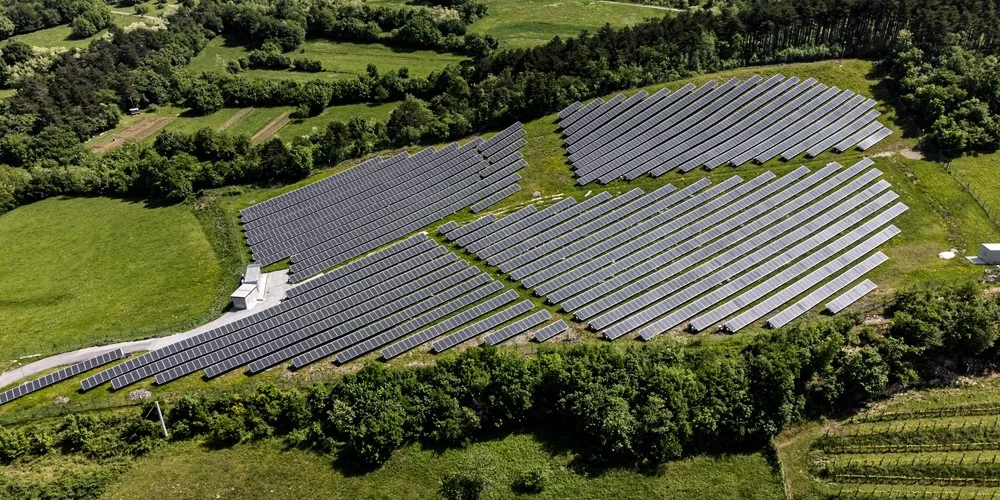
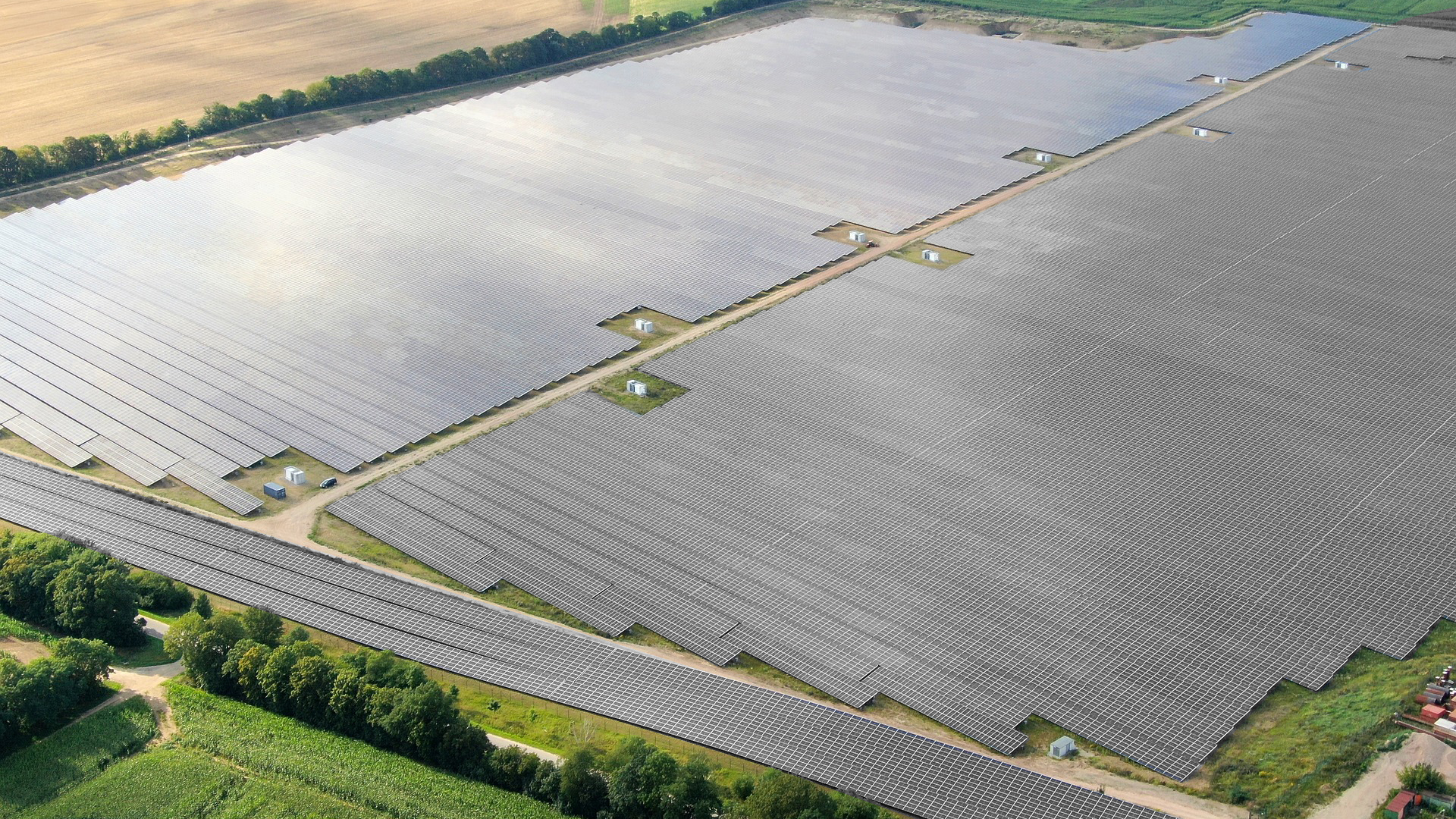
Solar farms are the workhorses of solar energy, taking up acres of land—sometimes thousands of acres—to produce clean energy for homes and businesses across the world!

Did you know that the sun produces enough energy in just one hour to meet the global energy needs for an entire year? The earth receives 430 quintillion Joules of energy from the sun every hour. That’s more than the 410 quintillion Joules that all of humanity uses in a year! Over the last decade, the use of solar energy has grown exponentially. Individuals and businesses are finding ways to maximize the production of clean energy. One effective solution for allowing people and businesses to take advantage of solar energy is a solar farm.
In this article, we will explore what a solar farm is, how to take advantage of a solar farm, and the associated benefits of joining a solar farm.
What is a solar farm?
A solar farm is a large area equipped with solar panels that harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. Also, these solar panels typically contain photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. Then it converts D into AC power for the electric grid by large inverters. They are typically mounted on structures on the ground. Solar farms are environmentally friendly.
Solar parks, solar projects, solar installations, and solar power stations are the other names for solar farms. These solar arrays are not like residential or commercial solar. Moreover, Solar farms operate more like conventional power plants, sending electricity directly to the power grid.
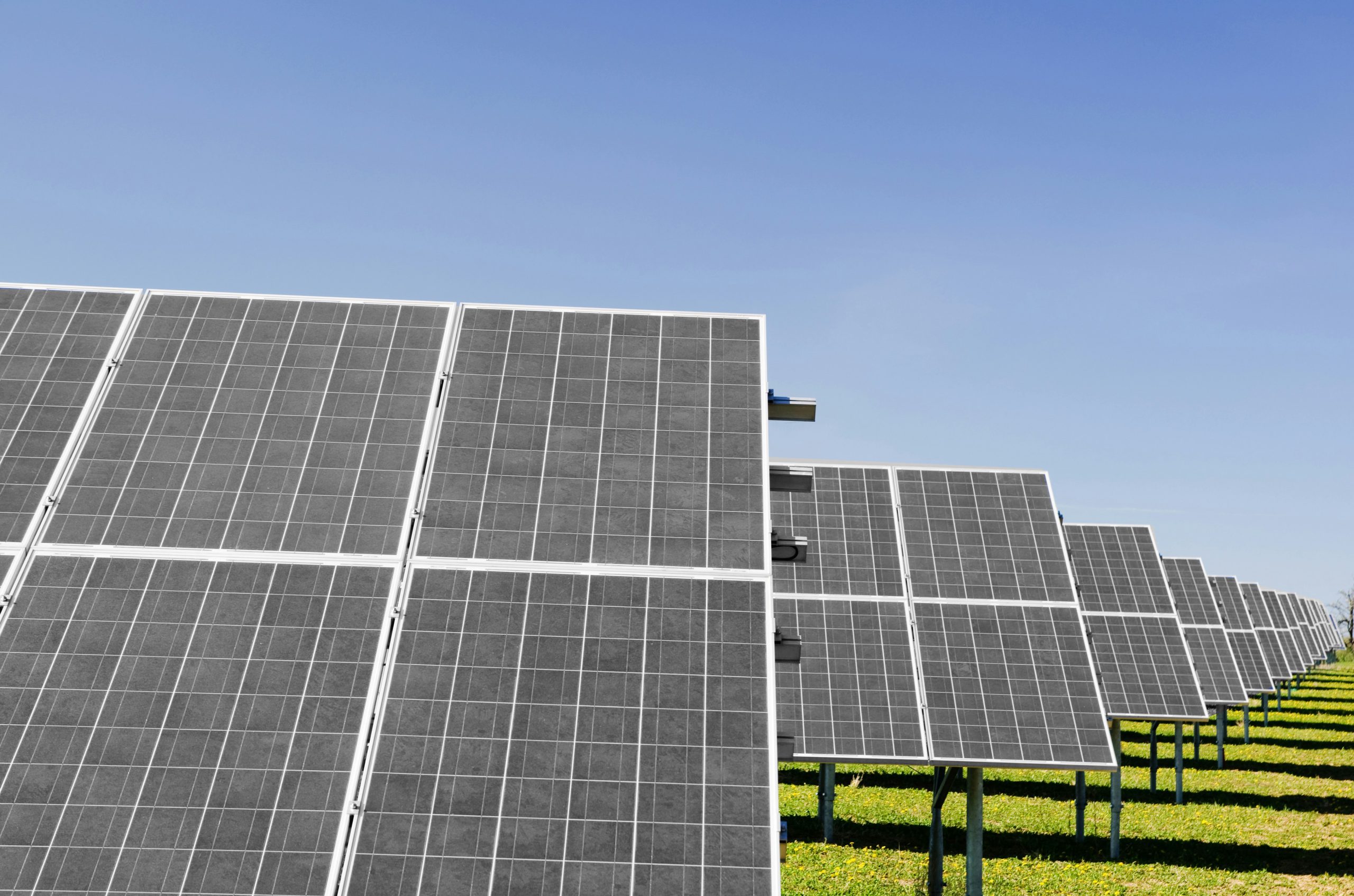

How does a solar farm work?
Solar farms utilize large swaths of empty land to capture sunlight with solar panels and turn it into electricity. The energy is then sent into the power grid and sold to customers, either under a power-purchase agreement (PPA), or as part of the power company’s energy mix. The landowner is compensated by the project owner(s) and/or electric company for the use of the land.
How much energy can a solar farm produce?
The energy output of a solar farm is contingent on its size, geographical location, and the efficiency of its solar panels. Solar farms can vary widely in capacity, with larger installations typically generating more energy. For example, the Longyangxia Dam Solar Park in China, covers square miles of land and produces an impressive 850 megawatts (MW) of energy daily. Similarly, the Desert Sunlight Project in California, a 550 MW solar farm, has been operational since 2011, producing power for thousands of homes and businesses every day.
Are there different types of solar farms?
There are two main types of solar farms: utility scale and community scale. Utility-scale solar farms sell the solar power they make to the electric company. The other type, community solar farms, sell power directly to people—like those who live in houses or apartments, and businesses. So, the big solar farms deal with electricity companies, while community solar farms provide power straight to regular folks who use electricity in their homes—often at lower rates than they can get from utilities.
● Utility-Scale Solar Farms
A utility-scale solar farm, commonly known as a solar power plant, is an expansive solar installation. These farms consist of many acres or square miles of solar panels and generate electricity that is fed into the grid. The power generated is sold at wholesale rates to utility buyers through power purchase agreements (PPAs). The utilities then distribute the electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial customers connected to the grid, generally as part of its energy mix.
● Community Solar Farms
Community solar farms allow households and businesses the opportunity to go solar energy without the need to install rooftop solar or solar panels on their own property. Community solar farms, also known as “solar gardens” or “roofless solar,” are solar power projects that generate electricity on behalf of the households and businesses that invest in the project.
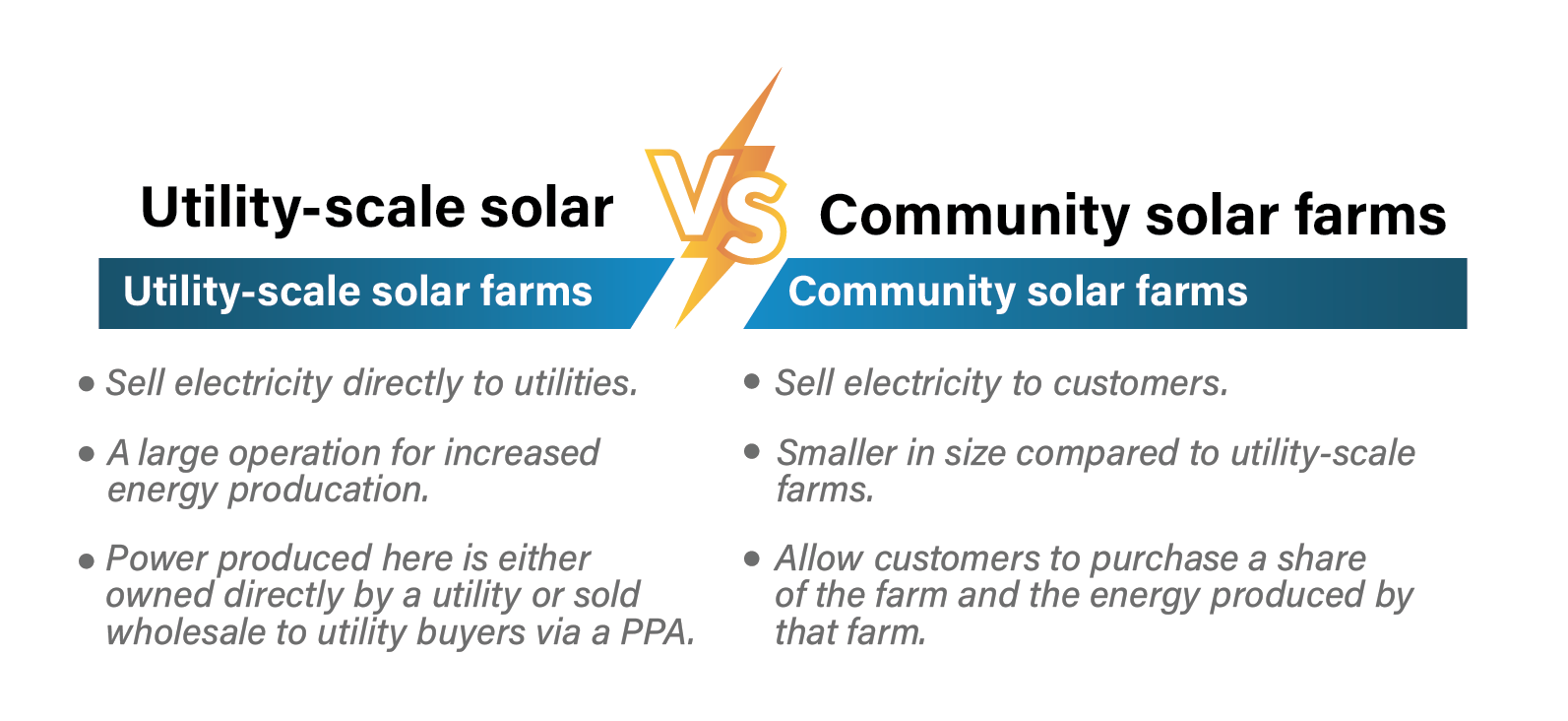
Typically, these solar arrays are ground-mounted and span several acres or more, often situated in open fields. They often range from 50 kilowatts to 5 megawatts. Like utility-scale solar projects, community solar farms put energy on the grid. However, the individuals and companies who get power from a community solar farm agree to either buy some of the project outright, or pay for the power that some of the panels produce in the project through a lease or subscription-type of arrangement. That allows them to benefit from the energy produced by the panels in the solar farm. Also, The power produced by the panels is often offered at a rate lower than that of the utility and can protect the community solar farm members from time-of-use and raising electric prices.
In many states, community solar subscribers can also take advantage of virtual net metering. This incentive enables the energy to credit back to subscribers as reductions on their electricity bills.
What are the benefits of a solar farm?
1. Maximize Efficiency and Biodiversity in Solar Project
Solar projects are strategically located based on solar radiation mapping, ensuring optimal energy production. Aso, Post-installation, eco-friendly designs can minimize wildlife impact, creating habitats for native species and promoting pollinators like butterflies and bees. Solar farms can also repurpose brownfields, former mines, or dumps for solar farms maximizing land use efficiency, transforming otherwise unusable areas into sustainable energy sources.
2. Dual Benefits for Renewable Energy and Sustainable Agriculture
Agrivoltaics integrates solar panels with agricultural practices, optimizing land use. Moreover, these sites are strategically designed to allow sufficient sunlight for crops beneath solar panels. Well-planned agrivoltaics systems conserve water, produce renewable energy, and sustainable produce.
3. Energy Generation and Self-Sufficiency
Solar panel farms generate clean and eco-friendly energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and helping curb greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, a solar panel farm promotes energy self-sufficiency. Landowners can generate an extra source of income by leasing to solar farm companies. Also, Installing a solar farm on agricultural land empowers farmers to become active participants in the clean energy revolution while securing their energy supply and reducing operational expenses.

4. Environmental Benefits
As more solar farms are installed they play an increasingly significant role in combating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability. By replacing fossil fuel-based energy generation with renewable energy, including solar power, we can reduce emissions of harmful climate-changing pollutants, like methane and carbon dioxide, as well as reduce the detrimental effects of mining for coal and gas on our environment. Additionally, solar panel farms reduce evaporation, thus conserving water resources. Agrivoltaics can optimize water usage and minimize the strain on water supplies.
How much does it cost to be part of a community solar?
If installing solar panels on your roof doesn’t work for you, joining a community solar farm is a great alternative. Unlike buying and installing solar panels on a building, signing up for a solar panel farm doesn’t necessarily require any upfront payment. Once you are part of a solar farm, you can expect to save around 5 to 15 percent on your electricity bill, thanks to the electricity produced by the community solar farm.
In many cases you can lease the solar panels or pay for the power from them through a power-purchase agreement. You may also opt to buy the panels in the farm outright and get the electric power they produce credited to your electric bill. To learn more about community solar gardens, see if your utility offers them or talk with a solar professional in your area.

Conclusion:
Here’s the cool part: every time you pass by, you can give a little wave and say thanks to those solar panels. They’re the reason you and your neighbors get affordable, clean power. It’s like a big thank you to the sun for helping us out!
If you want to learn more about solar or are interested in learning more about your options for solar at your home or whether an off-site option like a community solar farm is best, SolarSME is here to help you out.
Related Articles:
Commercial solar installation is a good option for you to take control of your electricity expenses and decrease your business operating costs.
There are approximately two billion gigawatts of community solar installed across the United States.
Sustainable energy solutions are now becoming important than ever because of the global climate catastrophe. A more sustainable future can be expected by using solar energy.



