- Updated On: July 29, 2025
Impacts of Different Weather
Conditions on Solar Efficiency
Solar panel output not only depends on the sunlight, but several factors may impact the solar efficiency, including rain, snow, humidity, etc. Although solar panels are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions like storms, hurricanes, and hail, however, their power generation may significantly vary depending on the environment. You might be wondering: how solar panels operate under various weather conditions, or ways to optimize the efficiency of your system? For optimal savings and efficient solar performance, it is essential to know how varying weather might influence your solar PV output.

Whether you are planning for solar installation or are already having a system, understanding weather parameters impacts on your system performance will help you make smarter energy decisions throughout the year.
What is solar panel efficiency?
Solar efficiency refers to how effectively a solar module can convert sunlight into usable electricity. The dimensions are simple: if a solar panel has 20% efficiency, it means it can convert 20% of the sunlight it receives into electricity. The most efficient in the market can achieve nearly 23% efficiency, a remarkable advancement from the solar modules of the initial solar trend, which were only 6% efficient.
Performance ratio is calculated by dividing the solar output by the energy they receive from the sun. The performance ratio is an easy way to measure the impact of different environmental factors on the production capacity of the panels.
How do the different climate factors affect the solar output?
Solar panels require direct sunlight to generate power; hence, they are installed on rooftops or grounds, and are impacted by the local climate, such as rain, hail, humidity, etc. Considering the climate of your area is also an essential factor while deciding about different solar brands and types in the market. Following are the major weather parameter that may affect the efficiency of a PV system:
Solar Irradiance:
The amount of solar energy per unit area receives is known as solar irradiance. It is the primary driver of PV performance. It determines the electricity production by solar panels. The sun changes its position throughout the day. Solar irradiance varies by factors such as time of day, geographical location, and atmospheric conditions. If there is high irradiance, your panels with receive more energy. Thus, the performance ratio of the panels will be highest, meaning they will generate more electricity. It is quite difficult to calculate the performance ratio of the panels when nearby objects cast shadows on the panels. But you can raise the solar irradiance by varying the optimal angle of the panel. In summer, the angle of tilt differs from the latitude angle of the location.
Moreover, this angel only deviates about 15 degrees in the winter. According to an estimation, a one-degree azimuth deviation from the south can cause a solar irradiation loss of 0.08%. Also, this can be improved by installing solar trackers with your system. Solar trackers can monitor the path of the sun to maximize the solar irradiance.
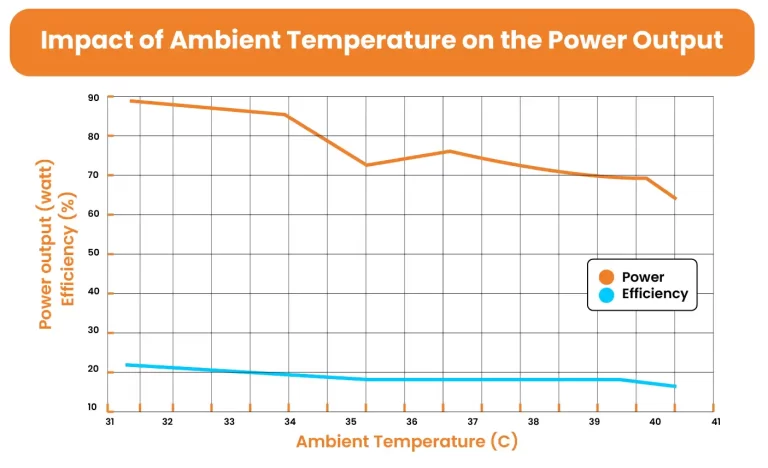
Ambient Temperature:
Temperature is an essential weather forecasting parameter that can significantly affect the power production of panels. Elevated temperatures can cause the semiconducting materials in the panels to become less efficient. At high ambient temperatures, the solar cells get heated up. This happens due to the negative temperature coefficient of solar panels. This means that under hot conditions, the PR value of the solar system will drop, reducing the overall efficiency of solar arrays. Without cooling, every 1 °C rise in solar cell temperature causes a 0.03–0.05% decrease in electrical efficiency. Moreover, at an operating temperature of 56 °C, the efficiency of solar panels decreases by 3.13% and the panel efficiency is reduced by 69% at 64 °C. Moreover, the temperature of surrounding also influences the solar panel’s voltage. The higher the temperature, the lower the panels’ voltage output.
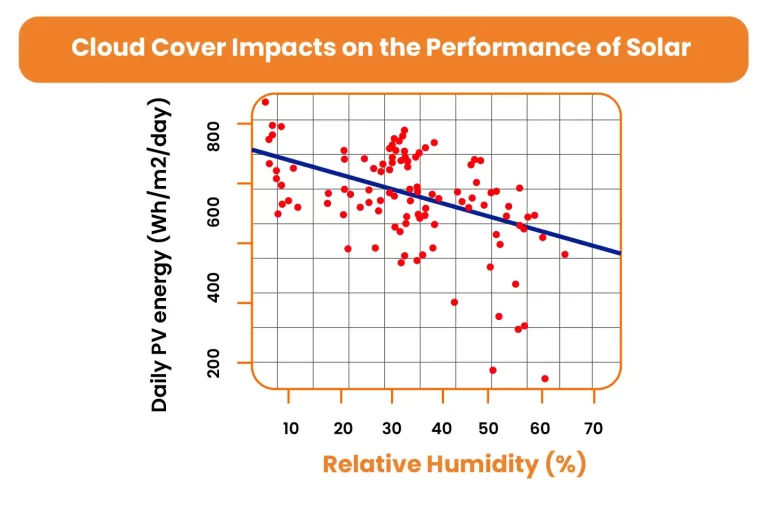
Cloud Covers:
Cloud cover is an important weather parameter that determines PV performance. Clouds absorb and scatter sun’s rays. Heavy cloud cover leads to a more decrease in the generation of electricity. However, solar panels on cloudy days too still generate power as some sunlight can pass through the clouds. Because of advance technology, solar panels are able to work well even on cloudy days.
Dust and Dirt Accumulation:
The settling of dust, dirt, and other elements on the surface of PV panels can lower the efficiency of the solar panel. These particles block the sun’s light from passing through to the semiconductor material, thus reducing energy to generate electricity. Dust settling is also dependent on conditions like humidity, rainfall, wind speed, origin, type, and model of solar panels.
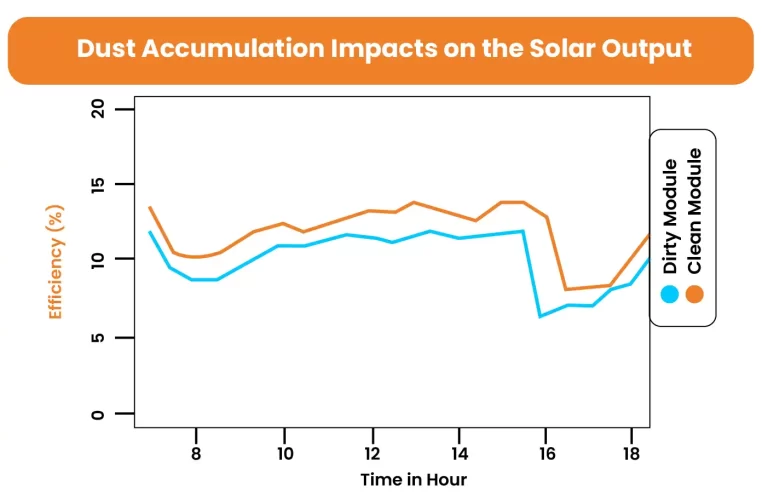
Moreover, in humid areas, dust particles can form an adhesive and sticky layer on the surface of the panels. According to an estimation, dust accumulation for 45 days can decrease the overall efficiency by 20%. However, regular cleaning and maintenance of PV panels is the key to ensuring optimal power production by panels. In dry and dusty, cleaning may need more frequently.
Humidity and Air Quality:
Humidity levels have a minor effect on PV performance. While high humidity can form dew on the panel surface, this effect has minimal impact. According to an estimation, if the humidity in the air decreases from 60% to 48%, the solar panel efficiency increases from 9.7% to 12.04%.
Additionally, a 20% increase in the humidity of the air may reduce the power capacity of panels by 3.16 watts. Polluted air also reduces the amount of sunlight received by the panels, therefore reducing electricity output. This effect is more prevalent in urban and industrial areas where there is higher pollution.
Soiling:
Soiling makes both hard and soft shading. Soft shading is occurred by smog, while hard shading is produced by the thickness of the soil on the surface of the panel. However, the power loss of energy from soiling depends on the geographical location. The panels with flat orientation and smaller tilt angles are more susceptible to soiling. By increasing the hydrophobicity, the dust accumulation on the surface of the panel can decrease. This will also increase the transmittance of solar radiation. You can increase the hydrophobicity of panels by changing the surface energy and roughness. Sprinkling water on the panels can also help you to reduce soiling effects.
Shading:
Solar panels are typically wired in a series, and shading one portion of a panel can reduce the power generation of the solar array. This is what is known as the “Christmas lights effect,” in which the shaded panel insulate the flow of current from the rest of the panels. However, designing and installing PV systems with minimal shading is critical to maximize power output.
In conclusion, if you want to maximize your solar power production, it is essential to consider the weather of your area before choosing a solar energy system. You can consider different types of PV module technologies in the market to compare the impact of dust and temperature on their performance, and to know which one of these technologies is more suitable for the local environment. Consulting with a local solar installer like Solar SME is preferable for a suitable solar system design to meet your energy goals.
Get a FREE Quote with our smart solar calculator to start your solar journey and power independence for the future!
Related Articles:
Although solar panels are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions like storms, hurricanes, and hail, however, their power generation may significantly vary depending on the environment. Explore how weather impacts on your system performance.
Installing solar panels is a huge investment. For many potential homeowners, the primary motivator to invest in a home solar system is the commitment to long-term savings.
In the United States, if you reside in a subdivision, planned community, or a building, you may be a part of the Homeowners Association, also known as HOA.


