- Updated On: June 03, 2025
How Do Solar Panels Work?
The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Solar Energy
Solar energy has become a popular source of power for homes and businesses in the United States. According to SEIA, there are over 5 million solar installations across the U.S., including residential, commercial, and utility solar projects. And this number is expected to reach 10 million by 2030. Solar owners are reducing their energy bills and enjoying the perks of grid independence by installing solar panels. However, many beginners are still curious: how do solar panels work to generate clean, renewable and unlimited power from sunlight?
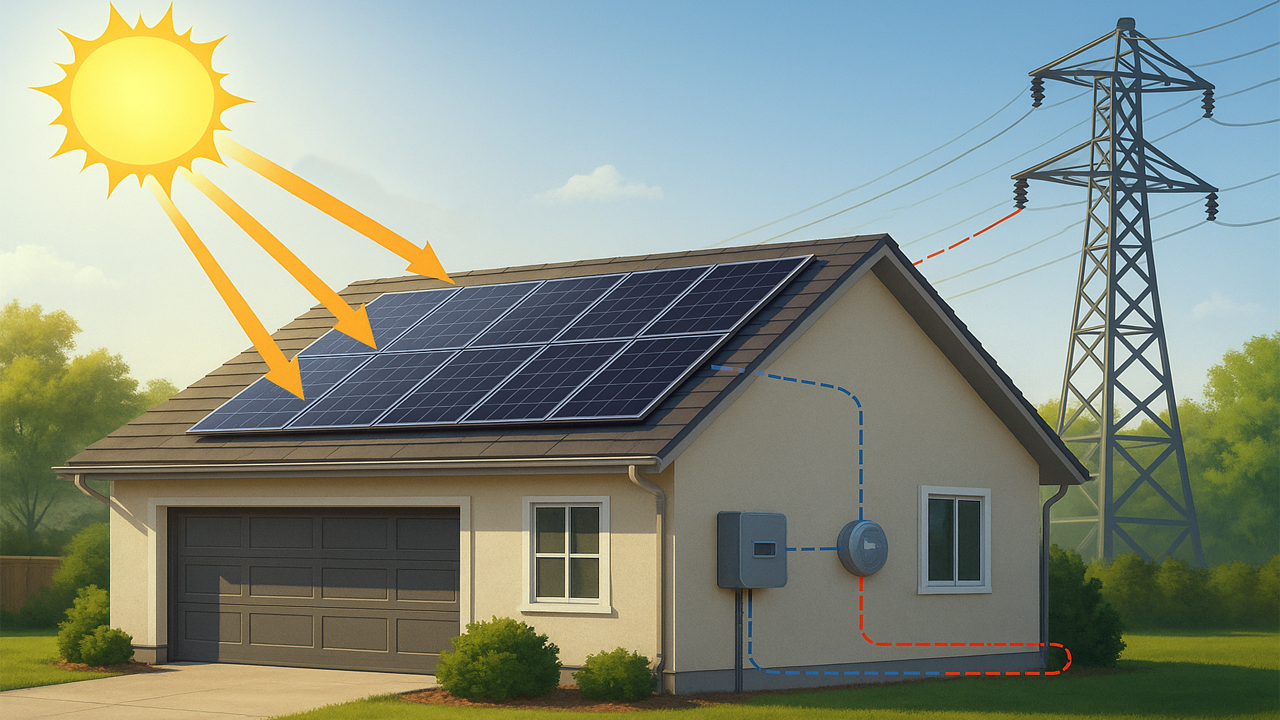
To maximize your solar benefits and savings, it is vital to understand the working of solar panels, and we are here to help you understand how solar photovoltaic (PV) panels produce electricity and why it is the best investment for your future.
What are solar panels made of?
One of the key elements of solar panels is silicon that is required to make semiconductors that convert solar energy into electrical power. Six parts are combined during the process to manufacture a functional solar panel:
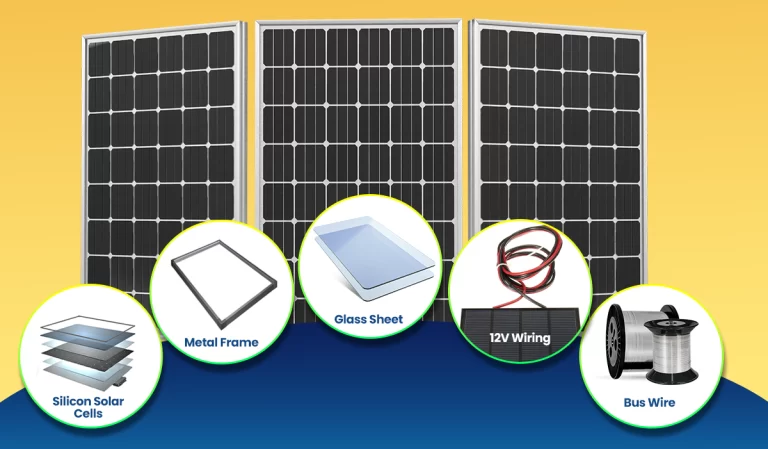
Silicon solar cells:
Silicon solar cells use the photovoltaic effect to turn sunlight into electrical power. The thin glass wafer sheet interacts with silicon cells, which are fused in a matrix-like arrangement between the glass panels, to produce an electric charge.
Metal frame:
The metal frame, which is commonly made of aluminum, provides structural stability to the solar cells. It holds the module while mounting on the rack. Also, the aluminum frame protects the panel from bad weather, like hail damage.
Glass sheet:
Despite being small, the glass casing sheet, which is typically 6-7 millimeters thick, plays an important role in protecting the silicon solar cells. To increase the longevity and safety of the silicon photovoltaic (PV) cells, a typical solar panel also has a glass shell at the front. The panel’s protective back sheet and insulation casing beneath the glass exterior help to reduce internal humidity and heat loss. Insulation is important because rising temperatures will reduce the efficiency and the output of solar panels.
12V wiring:
A 12V cable contributes to the sustainability and efficiency of the solar module by controlling the flow of energy into your inverter.
Bus wire:
The silicon solar cells are connected in parallel using bus wires. Bus wires are thick enough to transmit electrical currents and have a thin coating of soldering protection.
How do solar panels work for your home?
To generate direct current (DC) electricity, solar panels operate through a mechanism known as “the photovoltaic effect.” As the majority of home appliances do not use DC electricity, solar inverters transform it into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is usable in your home. Let’s break it down step-by-step:
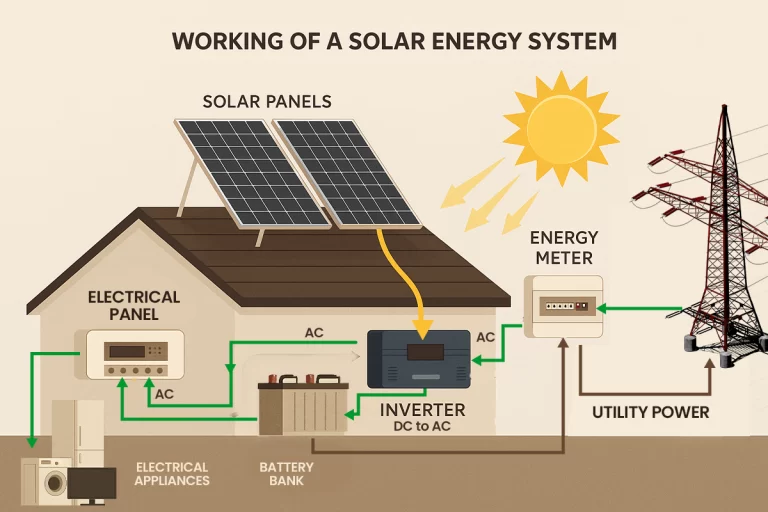
1. Two layers of silicon make up solar cells. Each is “doped” with phosphorus and boron to form the solar cell’s positive and negative sides, respectively. An electric field is produced at the border of the layers when photons strike the solar cells.
2. The atoms in solar cells are propelled into motion by this electric field, which knocks electrons out of them.
3. After passing through the solar cell and exiting the junction, the electrons produce an electrical current.
4. Metal plates on the sides of the solar cells detect electrical current, and it is sent to connecting wires.
5. Current flows through a wire to a solar inverter that transforms it into electricity that your house can use.
What are the key components of a solar panel system?
A residential solar panel system consists of the following components:
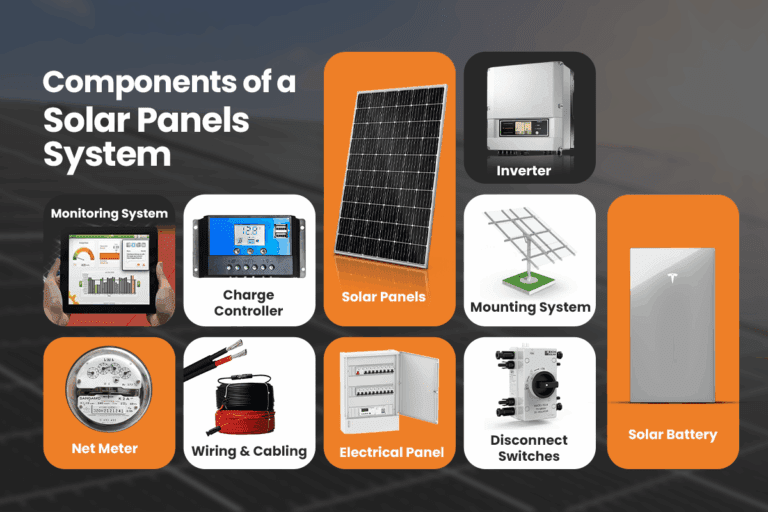
• Solar panels: The vital part that transforms daylight into power.
• Inverter: The device that converts DC power to AC power.
• Mounting framework: The structure needs to support the solar panels on the roof or the ground.
• Wiring and connectors: The electrical conductors that connect the solar panels to the inverter and the load (house, building, grid, or batteries).
• Bi-directional meter: The device that measures how much power the solar panels generate, consume, and send back to the grid.
• Solar Batteries: Not all systems have battery backups, it’s an optional that acts as energy storage which provides backup for night and during long power outages.
• Charge controller: For solar with battery storage systems, the charge controller regulates voltage and current flow from the solar panels into the battery. It prevents the battery from overcharging and getting damaged.
What are the different types of solar panels?
There are commonly three solar panel types available in the market. With technological advancements, new and more efficient solar panels like perovskite solar have also been introduced.
Monocrystalline solar panels:
They are made from silicon wafers, which are single, huge blocks of silicon. One step in the manufacturing process is cutting silicon wafers to attach them to a solar panel. The efficiency of monocrystalline silicon cells is higher than that of polycrystalline or amorphous solar cells. Individual monocrystalline wafers are more labor-intensive, which drives up the cost of manufacturing compared to polycrystalline cells.
Polycrystalline solar panels:
Polycrystalline cells are silicon cells; however, they are made by melting many silicon crystals together instead of forming them into a big block and cutting them into wafers. The panel is created by melting and then re-fusing many silicon molecules. Although they are less costly than monocrystalline cells, polycrystalline solar panels are less effective.
Thin-film solar panels:
Flexible solar panel materials, often in thin-film solar panels, are produced using amorphous silicon cells. Since amorphous silicon cells are not crystalline, they are affixed to a substrate such as metal, plastic, or glass. Unlike a typical panel, thin-film solar panels are slender and flexible. Compared to mono- or polycrystalline cells, amorphous solar cells are extremely inefficient.
How does sun exposure affect solar panel efficiency?
The efficiency of solar panels reflects how much sunlight they receive and convert into electric power. However, various factors like solar panel brands, type, roof orientation., may affect solar efficiency. Also, it is important to wisely decide between rooftop vs. ground-mounted solar according to your energy needs, space requirements, and sun exposure.

Hence, how do solar panels work based on your system design, size, equipment, location, etc. To maximize your solar output and savings, it is recommended to consult with a certified local solar installer like Solar SME. An expert solar installation company ensures the system is tailored according to your requirements to make your solar investment worth it for you. For an estimate, you can get a FREE Quote with our smart solar calculator!
Related Articles:
In the United States, homeowners and businesses are rapidly transitioning to solar power. Investing in solar is a great option to get rid of increasing energy bills for the future.
Solar panel cost is the key consideration. Learn how to make your solar journey more affordable even in the new solar tariffs era with best solar incentives and rebate programs!
In the United States, rising inflation, high energy costs, extreme weather, frequent power outages, and less grid reliance are the major reasons for switching to solar.