- Published On:
Bidirectional Charging: Is It Worth
It To Invest In EV Chargers?
What if your car could power your home during blackouts? Or, supply excess energy to the grid during peak hours? You’d earn credits or a discount on your electric bill. It’s possible with an electric vehicle (EV) equipped with bidirectional charging! As electric car technology evolves, we are near a gas-free future. Better batteries and faster charging are making EVs more viable. This constant development signals an all-EV future. Powerful batteries and efficient charging will replace gas-powered vehicles, and transform the transportation industry.

In this article, you will learn about bidirectional charging systems. You’ll learn how they work, and of their benefits for EV owners.
What is bidirectional charging?
A bidirectional charger is an advanced EV charger. It lets electricity flow two ways. Unlike a conventional unidirectional charger, a bidirectional charger is able to convert AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) when charging a vehicle.
Bidirectional EV chargers work like inverters. They convert AC to DC when charging, and DC to AC when discharging. These chargers require vehicles specifically designed to support two-way DC charging. The extra equipment to manage electrical loads and island a home during blackouts raises the cost of these chargers. For example, they use a bidirectional inverter, which lets stored EV battery energy power the house during outages.
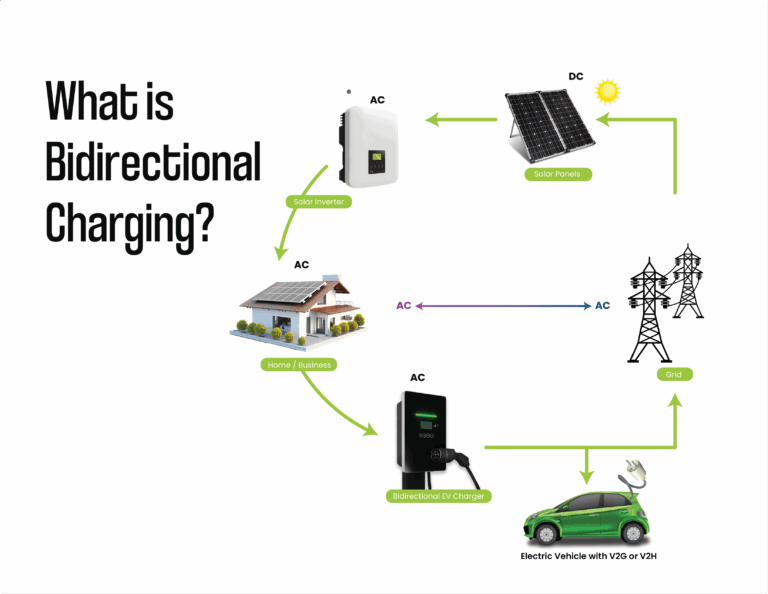
How does bidirectional charging work?
Bidirectional charging allows energy to flow from the grid to your vehicle and back, meaning your car can act as a backup power source for your home and the electrical grid. It includes two primary functions: Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G).
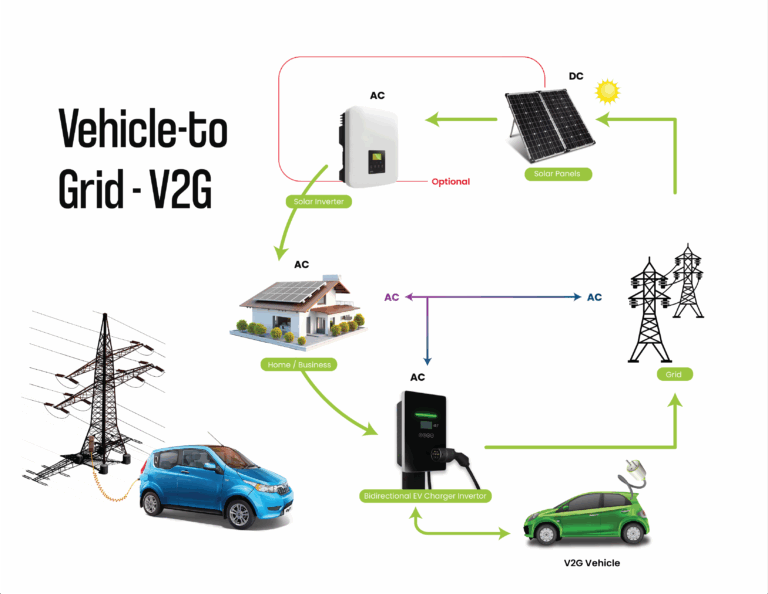
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
With V2G technology, the grid receives a small amount of EV battery energy when needed. V2G programs can give EV owners credits or savings on their electric bills. For example, EV owners can charge their vehicles during off-peak hours. They can sell excess energy back to the grid during peak demand. This could reduce their electricity bills. Learn more about peak shaving and off-peak savings.
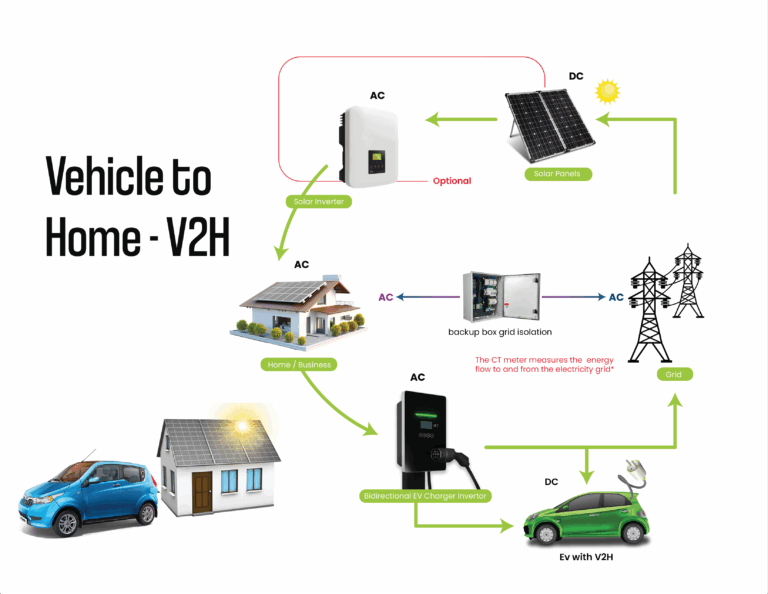
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H)
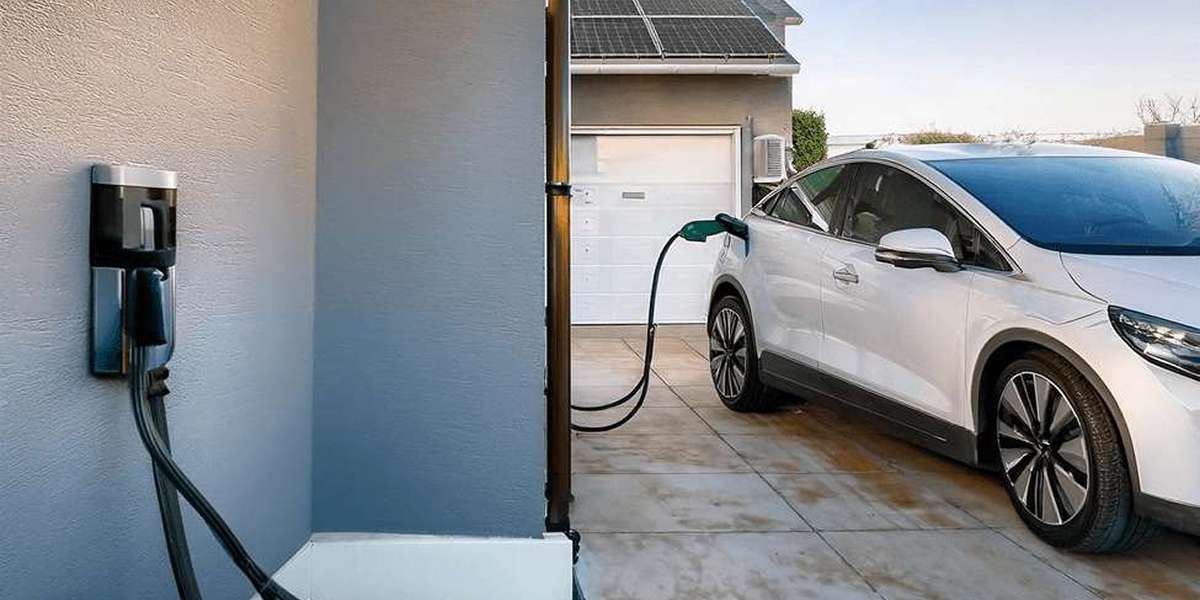
V2H technology lets an electric vehicle power a home, like a battery. During a blackout, the EV battery can supply backup power. Adding rooftop solar boosts benefits, allowing the car to charge with solar energy. When the home uses grid power, the CT meter signals the charger. It then draws the same amount from the EV battery. This method balances grid power consumption.
Different EV Charging Levels for Home and Business
Prior to considering an EV charging station installation, be aware of the different charging levels.
Level I EV Chargers:
These use standard 110-volt electricity and add a few miles of range to an EV per hour of charging. They are ideal for homeowners who have short commutes and can charge their vehicles overnight.
Level II EV Chargers:
It can increase an EV’s range by roughly 30 miles per hour while using 240-volt electricity. Both businesses and homeowners frequently utilize these chargers for quicker and more effective charging. Level II chargers are the ideal choice for home installation since they provide a nice mix between cost and speed. Are you curious about the cost of installing an EV charger at home? Learn about the cost to install an EV charger.
Level III or DC Fast Chargers:
The most potent chargers are Level III or DC Fast Chargers, which can reach a range of up to 100 miles in 30 minutes. Gas stations and fleet charging stations are examples of such places.
For household use, most homeowners choose Level I or II chargers. Businesses usually select Level II or III chargers based on their needs. Take a look at our commercial EV charging station installation services.
Our EV Charging Station Installation Process
At SolarSME, we make sure every EV charging station installation we deliver is efficient, safe, and reliable. Our process includes:
Consultation and Assessment: After analyzing the electrical setup of your house or place of business, we will recommend the most suitable EV chargers. Learn more about the cost to install an EV charger.
Installation: Our certified experts install and set up the EV charging station and verify it works at peak performance.
Maintenance: We provide ongoing maintenance services to keep your charger in peak condition. See our solar panel maintenance services.
Equipment We Install
We offer a variety of advanced equipment to suit different needs:
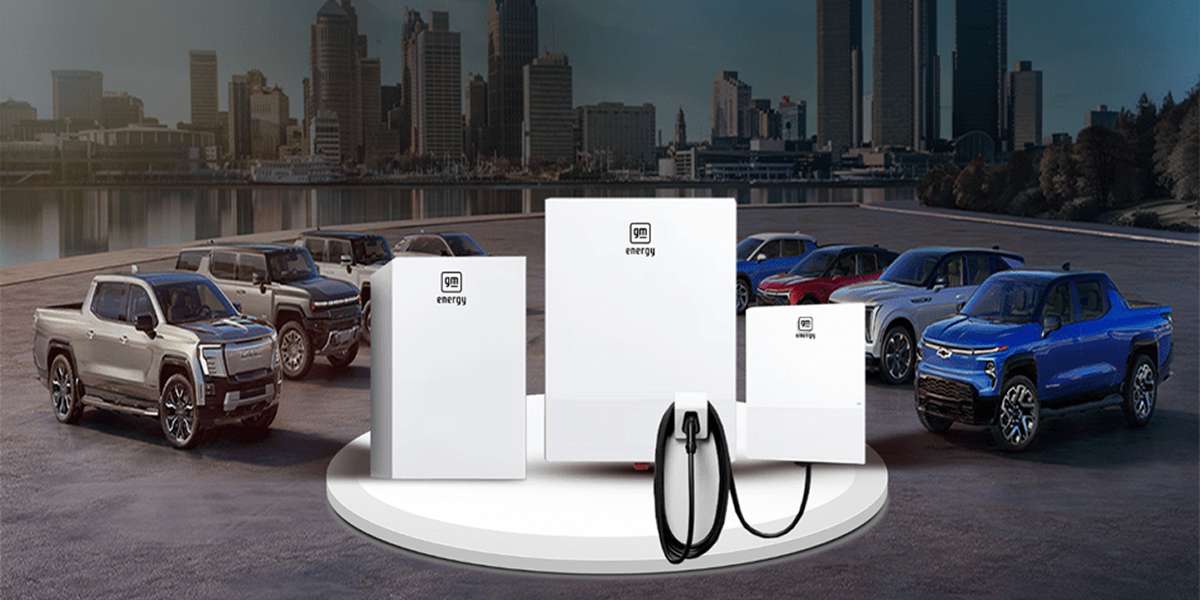
GM Energy PowerShift Charger:
A versatile bidirectional charger that integrates seamlessly with GM Energy systems to provide backup power to your home from your EV.
Enphase Bidirectional Chargers:
State-of-the-art technology for efficient bidirectional charging.
SolarEdge Bidirectional EV Chargers:
Reliable, high-performance chargers designed for both residential and commercial use. Regular EV chargers for efficient unidirectional charging.
Pairing your EV charger with battery storage or solar panels maximizes your energy savings and increases energy independence. Learn more about our battery storage solutions.
Do EV chargers work with solar?
Yes, EV chargers can work with solar energy systems. Although EVs consume more electricity than a typical solar system can provide in a single day, combining solar panels with an energy storage system allows you to store energy for EV charging when solar power is not available. Find out how EV charging through solar panels is the deal of the century.
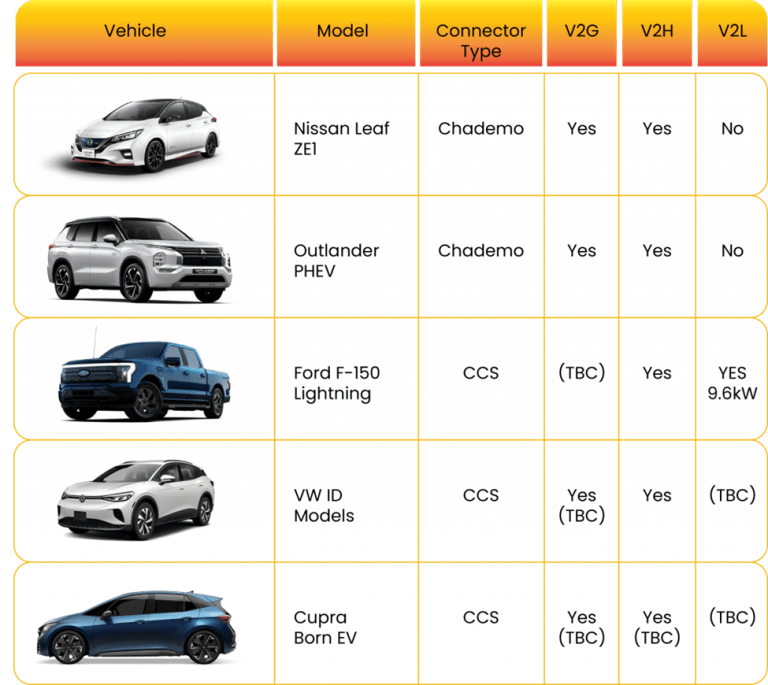
Vehicles with Bidirectional Charging Capabilities
Bidirectional charging technique is being used by several EV manufacturers. Among the well-known instances are:
General Motors Ultium EVs:
GM has already made bidirectional charging available for its Ultium-based EVs, supporting both V2G and V2H. Businesses and homeowners may effectively control their energy use with the aid of this technology. Take a look at GM’s bidirectional charging technology.
Note: GM presently provides a functional solution for bidirectional EV charging, while other manufacturers such as Nissan, Ford, Tesla, Kia, Hyundai, and Volkswagen are working in the development phase.
General Motors Ultium EVs:
GM has already made bidirectional charging available for its Ultium-based EVs, supporting both V2G and V2H. Businesses and homeowners may effectively control their energy use with the aid of this technology. Take a look at GM’s bidirectional charging technology.
Note: GM presently provides a functional solution for bidirectional EV charging, while other manufacturers such as Nissan, Ford, Tesla, Kia, Hyundai, and Volkswagen are working in the development phase.
Benefits of Bidirectional Charging for EV Drivers and Charging Station Owners
Save Money on Energy:
To save on electricity bills, use your car as a power source for your house and charge it during off-peak hours. Reselling excess energy to the utility company might further save costs with V2G technology. A study by the University of Rochester found that EV owners can save $120 to $150 annually with V2G chargers.
Store Backup Power:
An average electric car battery can store enough electricity to run a home for up to two days, making bidirectional charging a dependable backup power source during blackouts. Find out more about power outages and solar.
Portable Power Source:
Your car can be used as a portable power supply for emergencies or camping thanks to bidirectional EV chargers. If necessary, you can even charge other cars.
Bidirectional charging technology offers not only a way to power your vehicle but also an opportunity to provide backup power for your home, support the electrical grid, and potentially reduce electricity costs. Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner seeking the best EV charging station installation, Solar SME is here to help. Learn more about our EV charging solutions.
Related Articles:
With the increasing trend of using EVs, GM Energy V2H (Vehicle-to-Home) charging system is also gaining popularity.
The trend of electric vehicles is booming in the U.S. as an EV offer more sustainable and cleaner source of transportation.
With the advancement in technology, the world is moving toward a faster, better, and cleaner mode of transportation.