- Updated On: July 23, 2025
Comparing Types of Solar Panels:
Which One is Best for Your Home?
As the tax credit expires in 2026, many homeowners are planning to switch to solar with 30% lower solar installation expenses. If you are also searching for the best home energy panels, you may come across different types of solar panels in the market. Based on efficiency and performance, there are solar panels available including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin film, bifacial, etc. Each type has its unique characteristics, pros and performance metrics in different conditions. However, it may be challenging for you to choose the best solar panels to suit your energy requirements. Not all solar panels are same, and thus you have to be knowledgeable about each of their specifications to choose the right one for better efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run. Going solar is a smart investment, however, the solar panels and accessories you invest in directly impacts your system’s performance and future savings.

In this article, we will compare the major three types of solar panels in terms of cost, efficiency, and specifications and lead you through the right PV system for your house.
What are the primary types of solar panels?
There are 3 popular types of solar panels in the market including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. It will depend on your budget, energy goals and weather conditions in your area that which modules are suitable for your home.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels:
Monocrystalline solar panels are the common type of solar panels for roof installation today. The Czochralski process, wherein a silicon “seed” crystal is placed in a furnace of hot molten pure silicon, is utilized for making monocrystalline silicon solar cells. This makes one ingot, or a single silicon crystal, and then cut into thin silicon wafers, which we use in solar modules.

Polycrystalline Solar Panels:
One of the budget-friendly options for homes looking to add solar panels is polycrystalline panels, also widely referred to as “multicrystalline panels.” Polycrystalline panels also consists of silicon solar cells like Monocrystalline. The difference in making panels is how the panels are cooled, resulting in forming more than one crystal rather than one. Polycrystalline panels installed in homes typically contain 60 solar cells.

Thin Film Solar Panels:
Thin-film solar cells are primarily useful for utility and large-scale industrial solar installations as they have a lower efficiency rating. A photovoltaic material of a thin layer on top of a solid substrate, such as glass utilize to create thin film solar panels. The solar materials include cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon (a-Si). Despite the fact that each one of these materials produces a distinct “type” of solar panel, all are thin film solar cells.
Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline vs Thin Film Solar Panels: Which one is better?
Let’s compare different types of solar panels on the basis of some major factors to analyze which is more efficient and worth it for your home.
Cost: Which type of panels are more expensive?
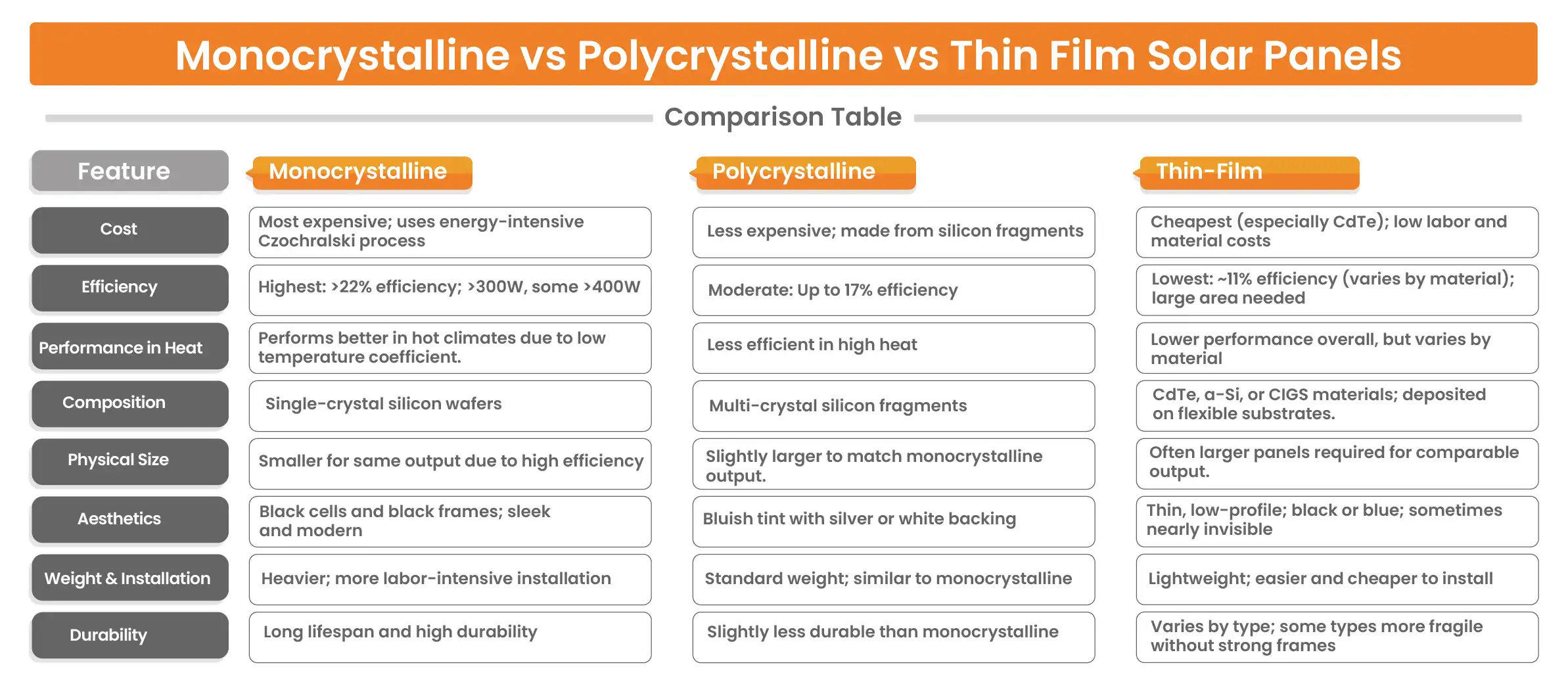
The cost of each type of panel varies due to variations in the manufacturing procedures. Monocrystalline solar panels are the most expensive among them. Making solar cells from a single crystal comes at a cost to the manufacturers. This Czochralski process, uses a lot of energy.
In contrast to monocrystalline solar panels, polycrystalline solar panels are usually less expensive. The cells are made of silicon fragments rather than single, pure silicon crystal. As a result, the production process for cells may be made considerably easier, which lowers costs for both producers and homeowners who install the panels.
The price of thin-film solar cells depends on the type of thin-film panel. In general, the cheapest type of solar panel to produce is CdTe. Compared to CdTe or amorphous silicon, CIGS solar panels are more expensive. Moreover, installing thin-film solar panels is less expensive than installing monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels. It requires less labor as the panels are lightweight and easier to move.
Efficiency: Which type of solar panels is more efficient?
Efficiency refers to the solar power output and it varies in different solar panels type. For maximum solar output and a limited roof space, high efficiency solar panels perform best. On average, monocrystalline panels have the best power capacity and efficiency. They have a power capacity of more than 300 watts (W) and can achieve efficiencies of more than 22. Conversely, polycrystalline solar panels often have lower wattages and rarely surpass 17% efficiency. Moreover, monocrystalline panels often outperform in hot climates and maintain better efficiency due to lower temperature coefficients.
Compared to monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels, thin-film solar panels have lower power capacity and efficiency. They are usually 11% efficiency rating, however it varies with the material type used for manufacturing. The size of a thin-film panel has a significant impact on its power capacity.
Composition: What are these solar cells made of?
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are made of silicon wafer cells. Manufacturers put wafer cells together in rows and columns to create a rectangle that is used to make a crystalline panel. After that, they frame the glass and place a sheet of glass over the cells. The silicon content of monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels differs. Monocrystalline solar cells require one silicon crystal for production. Manufacturers use a mold to melt silicon crystal fragments together to generate polycrystalline solar cells.
Thin-film solar panels, in contrast to monocrystalline and polycrystalline ones, can be made of several different materials. The most common kind of thin-film solar panel consists of CdTe, or cadmium telluride. Amorphous silicon (a-Si) can also be used for manufacturing them; this composition is comparable to that of monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. A common type of thin-film technique is copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). A conductive substrate composed of glass, nylon, aluminum, or steel is where the semiconductor material, composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenide, adheres in CIGS panels.
Aesthetics: What do different solar panel types look like?
If you see black solar panels on a roof, it’s most likely a monocrystalline panel. Due to interactions between light and the pure silicon crystal, monocrystalline cells look black. Most roofs look best with monocrystalline panels with black framing. Polycrystalline solar cells typically have a bluish tint as light bounces off the silicon fragments in polycrystalline solar cells differently than it does off a monocrystalline silicon wafer. Polycrystalline panels typically have either silver or white back sheets and silver frames. Compared to other solar panel types, thin-film solar panels are often smaller and have a low profile. They are often in black or blue color and hardly visible from the ground if installed on your roof. Thin-film cells are almost 350 350 times thinner than other types of panels.
What type of panel is right for your solar installation?
Each type of panel like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film has pros and cons, and the best option for you depends on your location and financial goals. Installing less expensive, lower-efficiency polycrystalline solar panels can save you up front if you have a lot of space for them.

We suggest high-efficiency, monocrystalline solar panels if you have limited space and wish to optimize your electric bill savings for the long term. The most popular application for thin-film solar panels is when building a portable or do-it-yourself solar system, such as on a boat or RV. For big, commercial roofs that cannot support the extra weight of traditional solar equipment, businesses also use thin-film panels. Due to their greater roof space, they may afford to install more panels with less efficiency.
In conclusion, solar panel technology has advanced over the past 30 years to increase durability, efficiency, affordability, and aesthetics. The modern solar panel market focuses on matching panel technology with the most economical and savings-driven application. Consulting with a trusted solar installer like Solar SME may help you choose the best solar solution according to your specific needs.
You can also Get a FREE Quote for estimating your solar savings with our smart solar calculator.
Related Articles:
You may come across different types of solar panels in the market. Based on efficiency and performance, each type has its unique characteristics, pros and performance metrics in different conditions. Explore each type and choose the right PV system!
Many solar brands in the market, making it a daunting task to choose the top-rated solar panels for home.
If you are searching for a budget-friendly and sleek rooftop energy system, Tesla solar panels are a good option. However, their efficiency rating is within the average range. So, if you live in a sunny state, you can choose them for aesthetics and cost-effectiveness. Explore the specifications and costs of Tesla solar panels. Also, we will compare them with other brands to help you decide about these panels.


