- Published On:
Understanding Smart Grid:
New Trends in Grid Modernization
The smart grid is a modern development of a traditional electrical grid. This new system uses digital technologies to connect the power utilities and the consumers. The power demand is booming as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources require electricity. Through the smart grid, an efficient and sustainable electrical power delivery system is made possible.

A Brief History of the U.S. Power Grid
The original US electric power grid was designed in 1882. It was planned mainly for the interconnection of other large power stations directly with homes and companies through HV lines. These earlier systems used D.C. over copper wires and were mainly run by fossil steam boilers and hydro turbines. Over time, the grid has evolved to accommodate new technologies and increasing energy demands.
Why is there a need for a smart grid?
With the current grid, it is not possible to meet today’s energy demands, and yet the power grid has been under constant development. Also, the increase in electric vehicles alone boost grid demand by about 25%. Furthermore, to cater this, we require a new type of grid – digital and computerized – that can manage the complexities of modern electricity needs.
How does the smart grid work?
The smart grid works as a bi-directional power flow system. The one major difference between the smart grid and the conventional system is the power flow. Also, the smart grid enables electricity to flow both ways, in contrast to the conventional one-way system that transmits energy from the power plant to the user. Moreover, to increase reliability and efficiency, this system uses cutting-edge technology. It includes Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS) and High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC).
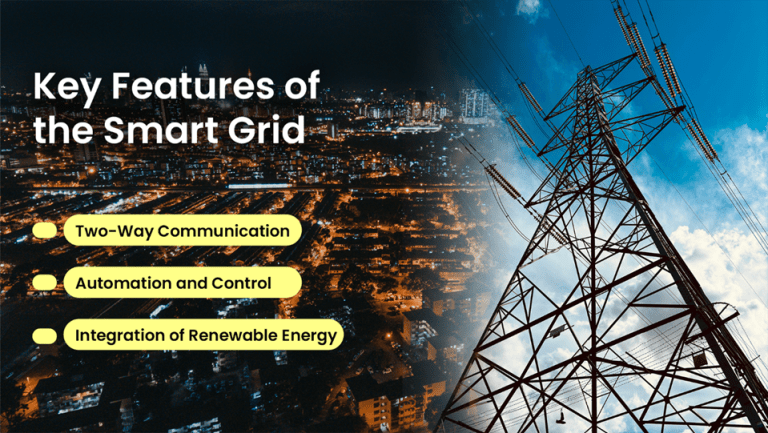
What are the key features?
- Two-Way Communication: The smart grid integrates digital technology for two-way communication between the consumer and utilities. This makes it possible to control and regulate power consumption and demand.
- Automation and Control: The setup of this grid consists of the control system, computer, and automation system. This enables it to detect and respond according to the electricity demand. This makes the system more efficient and reliable.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: IT facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Smart solar inverters convert the output DC power from PV panels into AC power which home or business use.
What are the benefits?
- More Efficient Electricity Transmission: The smart grid offers less waste of energy during transmitting or distributing the energy. Therefore, the system is more efficient.
- Improved Customer Service: Utilities can revert to power disruptions on time due to this grid system. It helps solving the issue more quickly.
- Cost Savings: These grid helps utilities cut down their operational costs which leads to lower power tariffs for customers.
- Enhanced Reliability: By detecting and isolating power outages quickly, the smart grid minimizes the impact of power disruptions and ensures faster recovery.
- Environment Sustainability: It promotes renewable energy sources like solar energy. Also, this helps to decrease the reliance on fossil fuels. Therefore, decreases the concentrations of greenhouse gasses.
What are smart meters?
Smart meters are one of the essential components of a smart grid system. These meters update the consumers and utility companies with electricity usage at one time. This real-time information enables consumers to control energy consumption and on the same note assists the utility companies to optimize the grid.
Also, smart meters allow consumers with solar panels to sell any excess energy generated back to the power company through solar net metering and become prosumers. Furthermore, this not only provides a financial incentive for the consumption of renewable energy resources but also assists in managing supply and demand on the grid.
What is the role of IoT in the smart grid?
A primary function of IoT in the smart grid is the connection of devices and various systems. IoT in smart meters allows utilities to remotely monitor the power quality supplied to the consumers, the power that consumers are using, and other issues in energy distribution and even outages.
For businesses, smart meters can help in understanding an organization’s usage of energy to optimize and modify any unwanted expenses. At home, IoT technology assists the consumer in controlling the usage of power efficiently.
What are the challenges and future developments in building smart grids?
There are many challenges in the construction of the smart grid, for example, new technology, tools, and legal framework. It requires the connections of the transmission lines and contracts on the purchase of electricity over and above consumers’ rights and participation between the federal government, state government, and local government.
However, to enhance the electric transmission system of the country, an agency known as the “Building a Better Grid” program was launched by the United States Department of Energy in January 2022. As a result of this project, wide use of sustainable energy will be more encouraged hence reducing the impact of climate change in the distribution grid.
Concluding, the smart grid represents a significant advancement in how we produce, distribute, and consume electricity. Also, by incorporating digital technology, automation, and renewable energy sources, the smart grid promises a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable power system. While the transition will take time, the benefits of a fully operational smart grid are clear: lower costs, improved service, and a cleaner environment. Moreover, as we continue to develop and implement these technologies, the smart grid will play a positive role in meeting the energy needs of the 21st century and beyond.
Related Articles:
Smart home technology is revolutionizing the way of living by allowing homeowners to manage their power usage and making their home efficient. Ever imagine you can control all your home’s appliances by using your smartphone. Learn More!
Microgrids are revolutionizing the current energy system because they provide an efficient, safe, reliable, and sustainable energy supply.
Solar panel technology is entering a new era, driven by innovative breakthroughs transforming the energy landscape.



