- Updated On: September 17, 2025
Solar Financing: Best Ways to Pay for Your
PV System Installation
Installing a solar energy system is a costly investment, but there is a reason why thousands of people turn to solar every year. A PV system installation is a smart home upgrade that can reduce your electric bill by as much as 95% and provide you with grid independence. With solar panels having a life of 25 years or more, long-term savings can be staggering. However, you may not be able to buy a solar panel system with cash. The good news is that there are several solar financing options to fit your budget and financial goals. The best option is to purchase in cash to achieve the highest long-term cost savings and all the solar incentives and rebates. However, if you can explore solar loan financing to spread the cost over time, or consider a solar lease or PPA to enjoy the benefits of energy with little or no upfront cost. Each option has its own advantages, depending on whether you like to own outright, keep payments to a minimum, or pay monthly.

As with any home renovation or improvement project, it’s essential to evaluate all of your solar financing options and choose the one that best fits your needs before installing solar panels. In this article, we will explore each option and its pros and cons to help you in the decision-making process.
What is solar financing, and how does it work?
Solar financing refers to the options to pay for a solar energy system. These flexible options help you switch to clean power with affordability. Owning a system is the best choice, which not only protects you from high power costs but you can also be eligible for federal and local solar incentives in your state. For example, investment tax credit is available till December 31,2025, to offset your total solar panel system upfront cost by 30%. However, it will be eliminated at the end of the year. Also, if you do not want to pay the full upfront, you can finance your solar panels with solar loans. Moreover, if this is not an affordable buying option for you, you can switch to solar with solar leasing/PPA financing. With no upfront cost, you can use clean power and reduce your high electric bills with this. But, as you are not the owner, you will not qualify for solar rebates and tax credits. Also, you need to pay a monthly installment to the solar leasing company. Although it is the least preferable option, you still save more as the monthly fees are comparatively less than your utility bills.
What are your solar financing options?
You can finance your home solar system in three ways: with a solar loan, a lease or power purchase agreement (PPA), or an upfront cash payment. However, a cash purchase or a solar loan are the two most economical options. A power purchase agreement (PPA) or lease is typically not a smart way, as despite spending thousands of dollars, you won’t own solar system at the end of the contract. Let’s have a look at each option:

Cash Purchase:
The most effective way to optimize your solar savings is to pay for your solar panel system using cash. For the next 25-30 years, your electricity expenses will be covered, and you won’t have to pay any extra interest like you would with a solar lease.You will pay a minimal amount as an electric bill with solar. You may protect yourself from potential rises in electricity rates by purchasing your system entirely. Additionally, you can take advantage of all the financial incentives and rebates that are available to homes that switch to solar power. The only thing to consider is that you may require a higher upfront cost, but the perks of owning a solar system, like a 30% federal tax credit, solar incentives and net metering(if available in your state), will support you with short payback periods and lower initial solar installation costs.
Solar Loans:
Since solar loans don’t require a down payment, they’re a good way to finance solar power systems if you can’t afford an upfront payment. The only drawback of taking out a loan is that you will have to pay interest, which makes it slightly more costly than paying out of pocket. However, if you have a good solar credit score, you will get lower interest rates, hence a reduction in total cost. And, the best part is that you will still own your solar panel system at the end of the loan period. But you should carefully review the terms and conditions of the loan, as carelessness can end up on the hook for additional fees. It is highly recommended to consult with a local solar installation company like Solar SME for the best option to finance your solar system.
Solar Lease/ PPA:
PPAs and solar leases often get mixed up as they are both forms of third-party ownership (TPO), in which a business installs solar panels on your property and then sells you the electricity the panels generate at a set price. You usually lock in a fixed electricity tariff with a lease or PPA. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, that rate should be between 10% and 30% less than the rate you currently pay for power. An annual rate rise, sometimes referred to as an escalator, is typically included in leases and PPAs. Under a lease or PPA arrangement, the company that owns the solar panel system will be the one eligible for any financial incentives and rebates related to solar, and you will not be. Furthermore, even though houses with solar usually sell for more than those without, this isn’t always the case with a lease or PPA because the new homeowner might not want to bear the extra monthly payment for the solar lease.
Cash vs. Loan vs. Lease: Which solar financing option is best for you?
Owning a solar energy system is not always a feasible option for everyone due to several factors, including limited budget, roof age, location, etc. So, it is vital to choose by analyzing all the contributing factors. Let’s have a look at all the ways to decide the right for you:
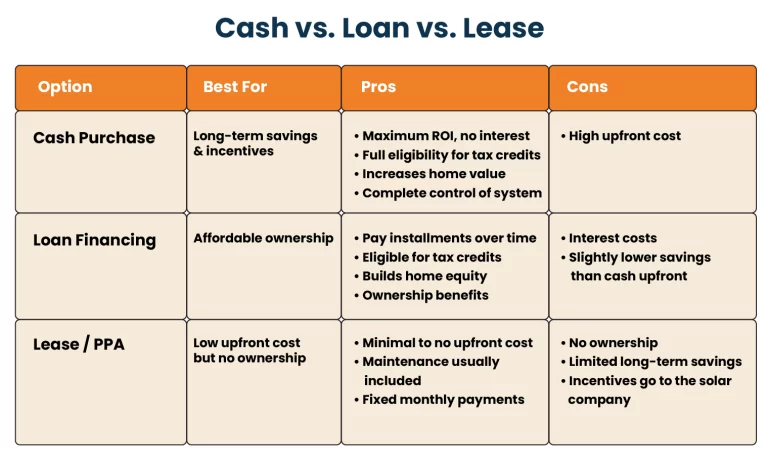
Invest in solar with a cash purchase if:
- You have enough money to pay cash upfront for a solar panel setup.
- You want to get the most out of switching to solar power financially. The best return on investment (ROI) for your solar system will come from a cash purchase.
- Before the ITC and other tax breaks and rebates expire, you want to take advantage of them.
- Your goal is to fully own your solar system.
Choose a solar loan option if:
- You want to own the system, but you don’t have sufficient cash on hand.
- You want to maximize your savings as much as possible.
- Take advantage of tax credits, net metering, SRECs, and all available solar rebates in your area.
Solar Leasing or PPA is good for you if:
- Your roof is not suitable for solar panels, or you are a renter.
- You are not interested in investing in a system for high ROI.
- Lower your energy costs without any upfront cost.
In conclusion, as the electricity costs and power outages are rising, solar financing options make it accessible to use clean power and maximize your future savings. Even if you cannot own a system, a PPA or solar leasing option leads to low electric bills and grid independence with $0 upfront cost. Whatever option you use, it is essential to understand all the important information before signing a contract. Contacting a trusted local solar installer like Solar SME can help you choose the best option for you.
The 30% federal tax credit is running out in three months, so if you are planning to buy a solar panel system, now is the right time. Get a FREE Quote with our smart solar calculator.
Related Articles:
30% federal tax credit is expiring in 2025. But if you missed out on it, you can still access solar power with Solar Lease/PPA financing. This option is an opportunity to get all the advantages of solar power while making no large initial investments. Explore More!
Solar panel cost is the key consideration. Learn how to make your solar journey more affordable even in the new solar tariffs era with best solar incentives and rebate programs!
It may require an upfront cost to install solar panels, however, there are various solar financing options. Explore the best option . between solar lease vs buy and make an informed choice.