- Updated On: June 20, 2025
Bifacial Solar Panels:
The Technology Behind Dual-Sided Power
Solar technology is evolving day by day, and now it is not just rooftop solar panels. Emerging technologies are designing solar modules to capture every sun ray and generate maximum possible clean energy. Bifacial solar is one of them. These modules are made up of solar cells that generate electricity on both sides of the panel. Bifacial solar panels are more efficient as compared to traditional monofacial panels. This is because they absorb sunlight from both sides of the module. For homes, they can work well with ground-mounted systems as compared to rooftop installations, which receive sunlight in only one direction. However, these double-sided solar panels are best for commercial or utility solar, as you can adjust them away from mounting surfaces, allowing sunlight to reflect into the back of the panel.

In this article, we will take a closer look at the bifacial solar panels. Also, we will compare bifacial vs. monoracial modules to guide you on which one is worth it for you.
What are bifacial solar panels?
Traditional panels, also known as monofacial modules, consist of solar cells that absorb sunlight to generate power from one side only. But bifacial panels are different as they can absorb light from both the front and the back because they have solar cells on both sides and are thus more efficient. Some of the best bifacial solar panels include:
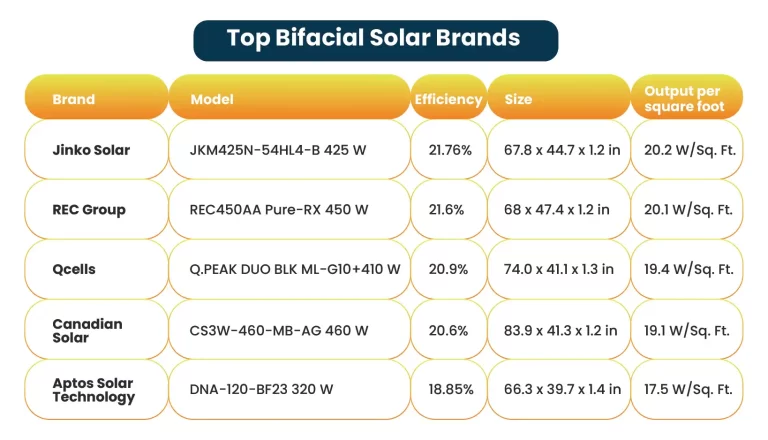
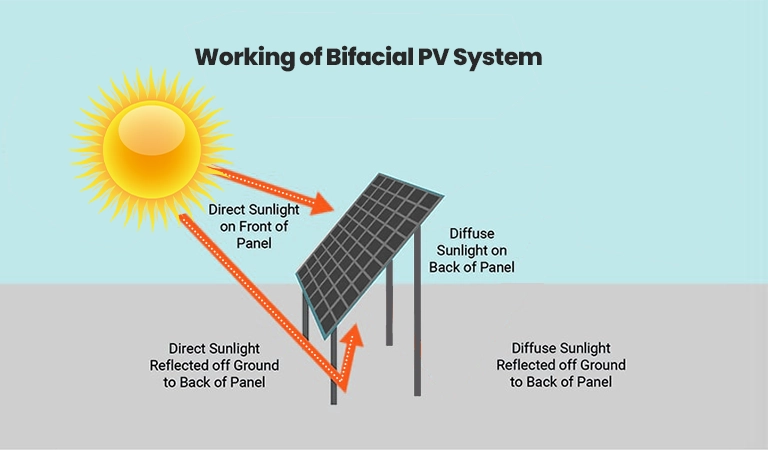
How does a bifacial PV system work?
These modules have solar cells on the front as well as on the rear side. It means that the back of the panel can also absorb light instead of wasting it.
Comparing Bifacial vs. Monofacial Solar Panels
Both types of panels have some differences in terms of cost, efficiency, and look. While choosing the panel type for your home or business, keep the following points in mind:

Efficiency:
Bifacial panels are typically more effective than conventional monofacial panels because they have a larger surface area accessible to absorb sunlight. For instance, bifacial panels generated 11% more energy than regular panels in a ground-mounted installation, according to a study conducted by solar panel manufacturer LONGi. This efficiency gain increased to 27% when used in conjunction with solar trackers, which modify the panel’s angle according to the position of the sun.
However, the installation environment affects the bifacial panel’s efficiency. Darker surfaces, like soil or asphalt, reflect less light than lighter ones, like sand, which reflects more light onto the back of the modules.
Appearance:
Between bifacial and monofacial solar panels, bifacial modules are slim. They are often encased in a thin, transparent layer of either a clear back sheet or a dual-glass design and have a small frame. Also, these panels require different solar mounting systems to optimize power generation from both sides. These systems usually use smaller junction boxes, narrower support rails, and vertical supports only at the racking system’s corners to reduce shading on the panel’s back.
Durability:
To increase durability against severe weather conditions like wind and hail, bifacial panels consist of glass on both sides. Furthermore, you can position bifacial panels vertically to gather sunlight at sunrise and sunset, two important periods of the day. Additionally, panels arranged vertically are less likely to accumulate snow and other debris, which can hinder the production of energy.
Cost:
Despite the benefits, the bifacial solar panel installation is higher than the standard rooftop system as it requires additional labor and special equipment. These modules only make sense when additional electricity savings outweigh higher equipment costs. Monofacial panels are, therefore, still the more economical choice for the majority of residential solar installations.
Are they worth it for residential installations?
Bifacial solar panels are commonly not suitable for rooftop installations, as the roof obstructs the panels’ backside. It will likely spend more on bifacial panels than the savings with an efficient traditional solar panel system. However, they may work better if you’re thinking about ground-mounted solar because they can capture light that is reflected from the ground. In a similar vein, they perform well on free-standing structures such as solar carports, where the panels may get sunshine from both sides because nothing is blocking their view.
Are bifacial PV systems a good option for commercial solar?
The best uses for these modules are in utility-scale and commercial solar projects. In this case, the panels are usually positioned above the ground so that sunlight can bounce off the ground below and enter the solar cells that face backward. Since they can boost energy output due to this additional light capture, they are a good choice for large-scale solar projects where efficiency is essential.
In conclusion, in the U.S. utility solar market, bifacial panels are expected to gain popularity due to their higher rate of energy output. For flat roofs, solar carports, and ground installations, they are a good option. However, bifacial solar panels are not a good choice for flush roof installations where their rear side would be hidden. As they are comparatively more costly, you incur greater equipment costs instead of savings and high ROI. However, businesses and utilities can use bifacial panels to maximize energy production per square foot.
Choosing the right solar panels is vital for achieving energy goals and maximizing future savings. Solar SME is a certified solar installer near you offering top-rated residential and commercial solar solutions tailored to your requirements. Our experts design an efficient solar energy system for you to boost your savings while achieving higher ROI and shorter payback periods. You can get a FREE quote with our smart solar calculator for estimation.
Related Articles:
You may come across different types of solar panels in the market. Based on efficiency and performance, each type has its unique characteristics, pros and performance metrics in different conditions. Explore each type and choose the right PV system!
Solar panel technology is entering a new era, driven by innovative breakthroughs transforming the energy landscape.
Many solar brands in the market, making it a daunting task to choose the top-rated solar panels for home.



